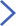
長(cháng)久以來(lái),化感(生物產(chǎn)生化學(xué)物質(zhì)從而影響另一個(gè)生物;Fig. 1)被認為能夠影響植物個(gè)體表現、群落結構與植物入侵。近期中科院東北地理所與農業(yè)生態(tài)研究所與德國康斯坦茨大學(xué)等單位合作搜集了384項實(shí)驗的數據,并首次對化感作用進(jìn)行了整合分析。結果表明,化感使植物的表現平均降低25%,但是研究間的異質(zhì)性很高。例如不同實(shí)驗方法測得的化感作用不同:與植物浸出液相比,植物殘余物的抑制作用較強,而化感植物土壤的抑制作用較弱(Fig. 2)。化感的抑制作用隨著(zhù)物種之間進(jìn)化距離(phylogenetic distance)的增加而增強,并且,已歸化外來(lái)植物的浸出液對本地植物的抑制作用強于本地植物的浸出液 (Fig. 3)。本研究表明化感作用確實(shí)可以促進(jìn)外來(lái)植物的成功入侵,而植物進(jìn)化距離與化感作用的關(guān)系表明了化感能促進(jìn)近緣種的共存(convergence)或促進(jìn)單物種在群落中占主導優(yōu)勢。在文章的最后,我們還就化感的促進(jìn)作用,土壤微生物對化感的影響,測試植物的重要性,以及化感的生態(tài)與進(jìn)化意義進(jìn)行了討論,希望給未來(lái)的化感研究提供一些線(xiàn)索。
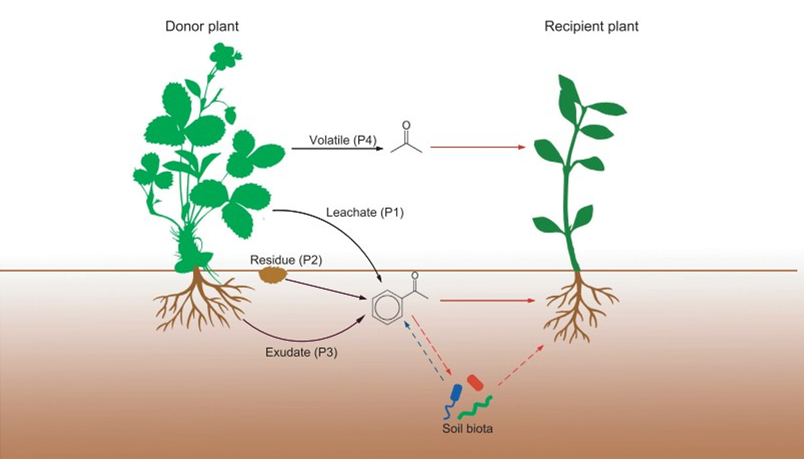
Figure 1 The different release pathways and effects of allelochemicals. The allelopathy plant (left) can release allelochemicals through four pathways (black arrows): leaching by rain (P1), decomposition of plant residues (P2), exudation from roots (P3) and volatilisation (P4). The allelochemicals can affect the test plant directly (red arrows) or indirectly through their effect on soil biota (dashed red arrows). Soil biota can also affect allelochemicals, such as through conversion or degradation of allelochemicals.
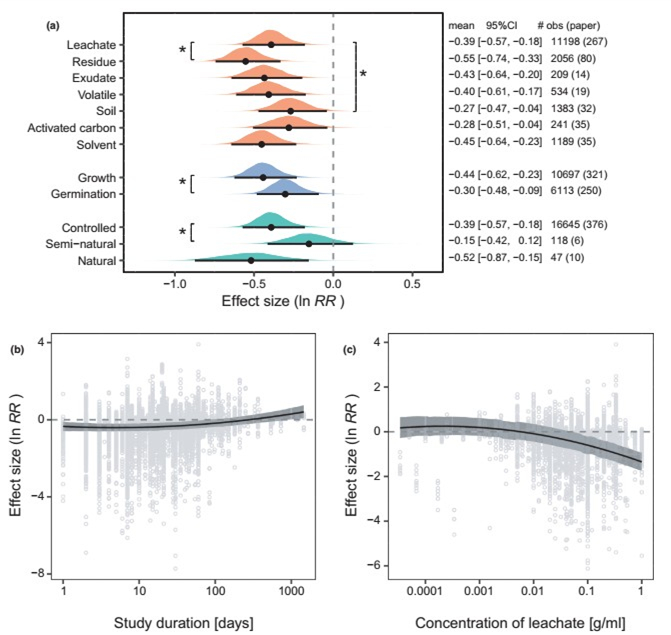
Figure 2 Effects of different aspects of study design on allelopathy. (a) Effects of the type of method (orange), the type of performance measure (blue) and the experimental environment (green) on allelopathy. (b) Effect of study duration on allelopathy. (c) Effect of the concentration of leachates on allelopathy. In (a) for each category (parameter), the posterior distribution is plotted with the mean and 95% credible interval. The text on the right displays the mean, 95% credible interval (CI), and the number of observations (obs) and papers. An asterisk indicates a significant difference between the level of interest and the reference level. In (b) and (c), curves of the estimated effects are shown with their 95% credible intervals. Negative values of the effect size (ln RR) indicate that allelopathy inhibits plant performance.
Figure 3 Effects of evolutionary history on allelopathy. (a) Effect of phylogenetic distance between allelopathy and test species on allelopathy. The curve of the estimated effect is shown with its 95% credible interval. (b) Effects of origin of allelopathy and test species on allelopathy when tested with the leachate method. Effects of native, non-naturalised alien and naturalised alien allelopathy species are shown in dark blue, light blue and orange. For each category (parameter), the posterior distribution is plotted with the mean and 95% credible interval. The text on the right displays the mean, 95% credible interval (CI), and the number of observations (obs) and papers. Negative values of the effect size (ln RR) indicate that allelopathy inhibits plant performance. An asterisk indicates significant difference between reference level (native on native) and the other.
該研究成果于近期發(fā)表在國際生態(tài)學(xué)Top期刊Ecology Letters上。本研究第一作者為張致杰博士,通訊作者為劉艷杰研究員。相關(guān)論文信息:Zhang Z, Liu Y*, Yuan L, Weber E, van Kleunen M (2020) Effect of allelopathy on plant performance: a meta-analysis. Ecology Letters, doi: 10.1111/ele.13627.
 上一篇:毛德華、馬群、周兵兵組織完成的Landscape Ecology專(zhuān)輯順利出版
下一篇:中國科學(xué)院東北地理與農業(yè)生態(tài)研究所馮獻忠團隊發(fā)現調控大豆類(lèi)胡蘿卜素含量的GmCCD4基因
上一篇:毛德華、馬群、周兵兵組織完成的Landscape Ecology專(zhuān)輯順利出版
下一篇:中國科學(xué)院東北地理與農業(yè)生態(tài)研究所馮獻忠團隊發(fā)現調控大豆類(lèi)胡蘿卜素含量的GmCCD4基因